Perhaps you already know that the iPhone uses a lithium-ion battery, but there are various types of lithium-ion batteries. For instance, there's the ternary lithium-ion battery commonly used in electric vehicles and the lithium polymer battery found in Samsung phones. So, what type of lithium-ion battery does the iPhone use?
What lithium battery does iPhone use?
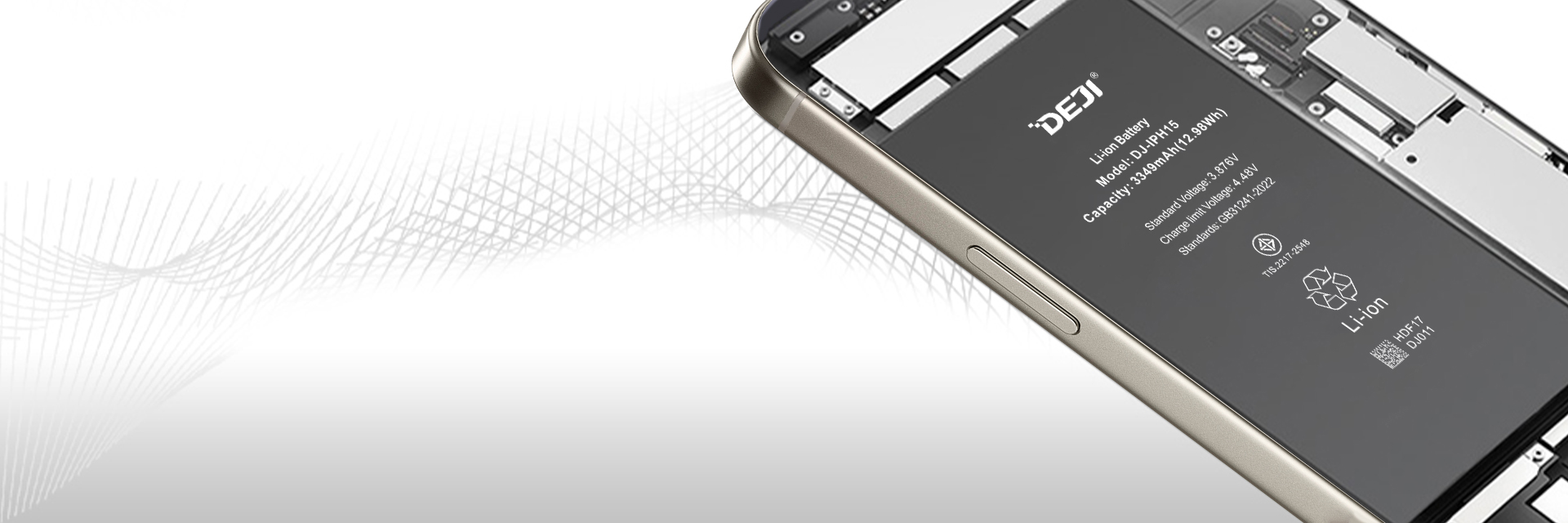
The iPhone uses lithium cobalt oxide batteries, specifically a type of soft-pack lithium-ion battery. It consists primarily of a positive electrode with lithium cobalt oxide and a negative electrode with carbon materials, along with an electrolyte containing various chemicals. What is the composition and working principle of mobile phone lithium batteries?

Initially, Apple incorporated lithium cobalt oxide batteries in their iPhone and iPad devices. The first-generation high-voltage lithium cobalt oxide battery was introduced with the iPhone 4, featuring a voltage of 4.2V when fully charged and a capacity of 155 milliampere-hours per gram. Subsequently, the iPhone 5 introduced the second-generation high-voltage lithium cobalt oxide battery, with specifications of a 4.3V voltage and a capacity exceeding 165 mAh/g. The latest iPhones are equipped with the third-generation lithium cobalt oxide battery, featuring a voltage of 4.4V and a capacity close to 175 mAh/g.
It's worth noting that the mentioned voltages are indicative of the battery's performance when fully charged.
iphone battery voltage
The iPhone battery voltage range is 3.8V-4.4V, which means the nominal voltage is 3.8V, and the highest charging cut-off voltage is 4.4V.

Regarding the nominal voltage, some lithium-ion batteries are marked as 3.6V/3.7/3.8V. All three are correct. If it is lower than this value, it means that the battery is in a power shortage state.
Why does the iPhone battery use cobalt? Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium Cobalt Oxide Batteries
Cobalt is a metallic element with the chemical symbol Co. It boasts excellent resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and magnetic properties. The primary application of cobalt is in lithium-ion batteries, and the cobalt used in these batteries is recyclable, contributing to environmental preservation. In April of this year, Apple announced its commitment to using 100% recycled cobalt in all batteries by 2025, further emphasizing its dedication to environmental sustainability. Like the original battery, the iPhone battery produced by DEJI also uses lithium cobalt oxide battery.

The combination of cobalt with lithium materials forms lithium cobalt oxide, the first widely used positive electrode material in lithium-ion batteries for electronic devices. Apple's success is partly attributed to the design of lithium cobalt oxide batteries, which offer significant advantages:
1. Lithium cobalt oxide batteries have a very high energy density, providing higher voltage and current.
2. They exhibit excellent impact and vibration resistance, enduring more stress and mechanical deformation.
3. Lithium cobalt oxide batteries have high safety standards, with good heat stability, preventing combustion or explosion during use.
4. They have high charge and discharge efficiency, allowing for rapid charging.
5. Lithium cobalt oxide batteries have a very low self-discharge rate, providing a more stable power source.
6. They are lightweight and occupy minimal space, effectively reducing the weight and size of electronic devices.
7. No memory effect: No significant voltage changes during charge and discharge processes, with no safety hazards.
Although lithium cobalt acid battery is powerful, in the face of the evolving electronics industry, it, like nickel-metal hydride batteries, still has unchangeable shortcomings. For example, lithium cobalt acid batteries are more expensive because of higher production costs than other batteries, they are easily overcharged or over-discharged at low temperatures, the cycle life can not meet the user's expectations, and discharge capacity is lower than theoretical values.
 sales@batterydeji.com
sales@batterydeji.com