In the world of lithium batteries, a small yet crucial component called the "tab" plays a pivotal role in the battery's efficiency and safety. Often overlooked, tabs connect the battery's core to external circuits, enabling energy flow. This article explores the vital functions of tabs, their materials, and applications, shedding light on the sophisticated engineering behind modern energy storage technologies.
What is the "tab" in a lithium battery?
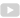
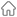
Lithium batteries, widely used for their high efficiency and capacity, incorporate a component known as the "tab." This is the protruding part where the battery's anode and cathode materials connect to the current collector, typically made from metal strips. These strips are either welded or adhered to the electrode sheets of the battery. During the assembly process, tabs are connected to the external circuit of the battery, enabling it to charge and discharge effectively.
The Importance of Tabs in Lithium Batteries
Tabs play a crucial role in the functionality and safety of lithium batteries. They serve as the interface between the battery's anode and cathode, facilitating electrical conduction, securing the core, and preventing short circuits:
1. Electrical Conductivity: The conductivity of a tab is a key indicator of a lithium battery's quality. During manufacturing, chemicals like lithium cobalt oxide and lithium iron phosphate are coated on the anode and cathode. These substances need to connect through the tab to the battery core to transfer charge. Poor conductivity in tabs can lead to inefficient charge transfer or interruptions, impacting the battery's performance and lifespan.
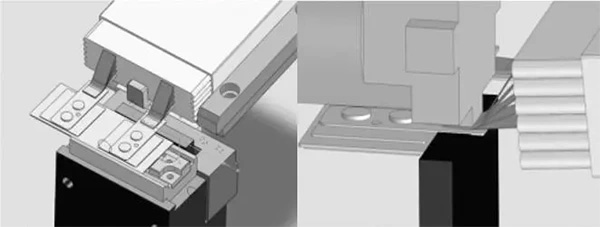
2. Securing the Battery Core: Tabs help prevent the battery's core from shifting or detaching during use. In battery manufacturing, the anode and cathode are bonded to the core, and the tab, serving as the connection point, secures the core within the battery. This prevents gaps between the core and the battery casing, thus avoiding short circuits and ensuring the battery's safety and stability.
3. Preventing Internal Short Circuits: During operation, if a short circuit occurs between the anode and cathode, it could lead to excessive current flow within the battery, generating heat and potentially causing fires. The design of the tab prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode, thereby avoiding short circuits and ensuring battery safety.
Why Different Materials for Tabs?
The positive tabs in a lithium battery are usually made of aluminum alloy, while the negative tabs are made from nickel or nickel-plated copper, each tab consisting of two adhesive films and a metal strip. The choice of aluminum, nickel, and nickel-plated copper as materials for tabs is not arbitrary:
1. Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum alloy, nickel, and nickel-plated copper offer excellent conductivity, providing better pathways for electron transfer.
2. Corrosion Resistance: These materials are highly resistant to corrosion, effectively withstanding oxidation-reduction reactions and chemical degradation, thus extending the battery's service life.
3. Mechanical Strength: Their high mechanical strength is essential for bearing the battery's weight and enduring vibrations, which guarantees the battery's stability.
Applications of Battery Tabs
Tabs made of nickel are primarily used in smaller digital batteries such as mobile phone batteries, portable power banks, tablet batteries, and batteries for smart devices. Meanwhile, nickel-plated copper tabs are mainly used in power batteries and high-rate batteries.
Conclusion
Tabs are integral to the performance and safety of lithium batteries. Their design, material composition, and application are critical for ensuring the efficient operation and longevity of these batteries. Understanding their role highlights the sophisticated engineering behind today's energy storage technologies.
 sales@batterydeji.com
sales@batterydeji.com