Understanding how to properly charge and discharge these batteries is crucial to maintaining their performance and longevity. Overcharging and over-discharging are two common issues that can significantly impact a lithium battery's lifespan and safety. This article explores what these terms mean, their effects on battery health, and practical tips on how to avoid them.
Overcharging of Lithium Batteries
Overcharging occurs when a lithium battery's charging voltage exceeds its maximum cut-off voltage, typically between 4.2 and 4.4 volts (for cell phone lithium-ion batteries). This can lead to changes in the structure of the cathode material inside the battery, resulting in a loss of total capacity. Overcharging can also cause the electrolyte to decompose and produce gases (e.g., hydrogen, oxygen), increasing the internal pressure of the battery, which may result in swelling, leakage, or case rupture.
Can I overcharge my cell phone by charging it for a long time?
Contrary to popular belief, charging a smartphone for an extended period does not lead to overcharging, thanks to the charging protection in the phone system, the BMS in the Li-ion battery, and the fast charging protocol in the charger.

Charge protection for smartphone systems
Some smartphones, such as the iPhone, provide optimized battery charging and temperature management in the system to prevent overcharging and slow battery aging. For instance, the “Optimize Battery Charging” feature introduced in iOS 13 and later versions learns the user’s charging habits and pauses charging at 80% or reduces the charge current until the user is predicted to need the device.
BMS in Cell Phone Lithium Battery
The BMS built into the cell phone's lithium battery can monitor the battery's voltage, temperature, and charging status to ensure the safety of the charging process. Once the battery is full, the system will automatically stop charging to prevent overcharging.
Fast Charging Protocol in the Charger
Original chargers support QC (Qualcomm Quick Charge) and PD (USB Power Delivery) protocols, which allow the charger to communicate with the phone and adjust the current and voltage according to the phone's needs.
Charging Stages of Phone Lithium Batteries
A cell phone's Li-ion battery is charged using the charger in two stages:
- Constant Current Charging (CC): When the battery has a low charge percentage (and low voltage), it is charged at a constant current and the voltage gradually increases.
- Constant Voltage Charging (CV): When the battery voltage is close to the maximum rated voltage (e.g., 4.2 volts), the charger switches to constant voltage charging, with a gradually decreasing current until the current drops to a smaller value (usually the termination current), indicating the end of charging.
In summary, with the triple protection of the phone system, the lithium battery, and the charger, the cell phone will not be overcharged during charging. However, you should still try to avoid charging the cell phone for excessively long periods, as this can cause calendar aging of the battery.
How can I prevent my cell phone battery from being overcharged?
If your phone and accessories are original, you do not need to worry about overcharging the lithium-ion battery. However, if you are using third-party accessories, you need to pay attention to their quality.
- Replacement of Lithium Batteries: It is recommended to choose a high-quality cell phone battery. Although very cheap and shoddy batteries may have a BMS, they are prone to fail during use, causing the battery to swell shortly afterward.
- Third-Party Chargers: Choose a certified charger. Many third-party manufacturers now produce chargers that support QC and PD protocols, making them as safe to use as the original.
Over-Discharging of Lithium Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries release stored energy during use. When the discharge voltage falls below the cut-off voltage specified by the manufacturer (usually 2.5V or 2.8V), the battery is considered over-discharged. Frequent over-discharge accelerates battery aging, shortens battery life, and can cause the battery to generate excess gas and heat internally, leading to swelling or leakage.

Is discharging a cell phone until it shuts down over-discharging?
A battery level below 0% is not over-discharging. The energy stored in the battery is usually more than what the phone system displays. This means that when your phone shows 0% battery, the actual charge in the lithium battery might still be around 5%, with a voltage above the minimum cut-off. Therefore, over-discharging does not occur. When the phone shuts down due to low battery, it is the Battery Management System (BMS) at work. The BMS automatically cuts off power when the battery level gets too low to prevent damage.
However, frequent deep discharges will lead to a gradual decrease in the capacity of the lithium battery. The active substances in the battery will be irreversibly lost during deep discharge, resulting in lower battery capacity and shorter cycle life.
Want to extend the battery life of your cell phone? Read our previous post: 4 Charging and Discharging Guidelines to Maximize iPhone Battery Life
Conclusion
By understanding the concepts of overcharging and over-discharging, users can take proactive steps to prevent these issues. Utilizing original chargers and batteries, leveraging the built-in protections of modern devices, and following recommended charging habits can help maximize battery performance and longevity.
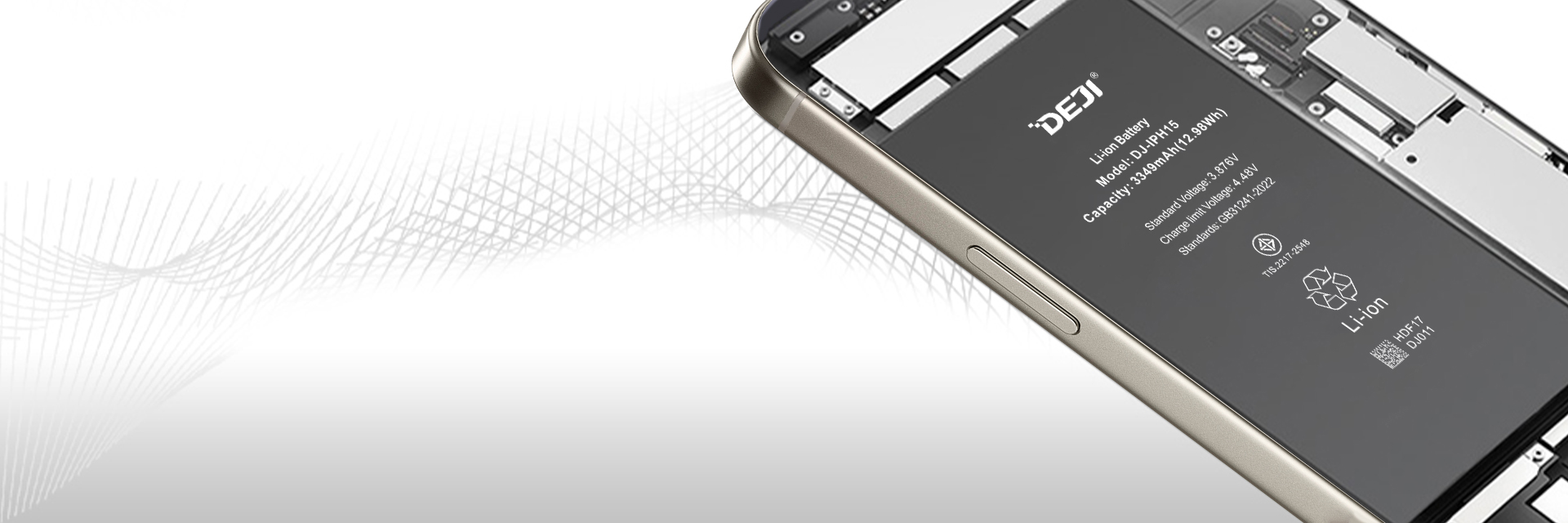
Do you need help? We are DEJI, a professional mobile phone battery manufacturer. Our latest product, the DJ battery, is made from the highest quality raw materials and can display a 100% health status.
 sales@batterydeji.com
sales@batterydeji.com